Types of adenotomy. Cold plasma adenotomy. Classic adenotomy.
Author: Dr. İsmayıl İ. Category: Nose
Published: 2023 - 22 - Jan
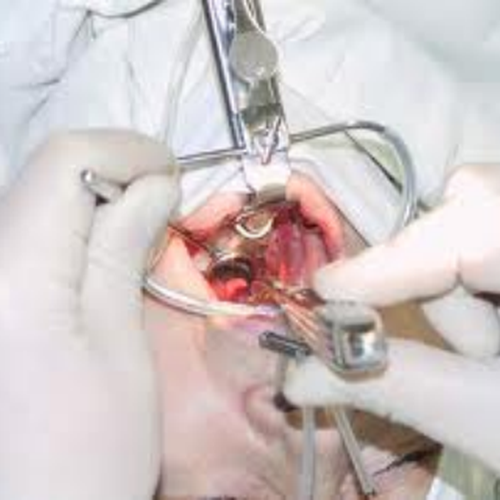
With classical removal, the doctor has the opportunity to calmly and without haste remove the adenoid tissue with a conventional adenoid and under visual control using a laryngeal mirror.
Raising the soft palate with a special instrument, he carefully examines the nasopharynx, the presence or absence of adenoids, supplementing the examination with a digital examination. The operation is accompanied by bleeding, usually minor, which is easily stopped by pressing the turunda on the nasopharyngeal tissue for 2-5 minutes, it is rarely necessary to use additional methods to stop bleeding (radio wave or laser cauterization, powdering of special powdered hemostatic drugs).
There are radio wave adenotomes that simultaneously remove adenoid vegetations and coagulate the injured tissue.
The cold plasma technique uses the principle of cold plasma (coblator). This is the most modern method in otorhinolaryngology. The peculiarity of this operation is bloodlessness, the possibility of a more complete removal of adenoid tissue.
An important addition to these techniques should be endoscopic control through special optical systems during the operation. Only in this case can you be sure of the complete removal of the adenoid tissue.
Another topical question that almost all parents ask is that adenoids may reappear after surgery. Unfortunately, relapses (re-growth of adenoids) are quite common. It depends on a number of reasons, the main of which will be listed below.
The most important thing is the quality of the operation. If the surgeon does not completely remove the adenoid tissue, then the adenoids may re-grow. Therefore, the operation should be performed in a specialized pediatric hospital (hospital) by a qualified surgeon. This allows you to completely remove the adenoid tissue. However, if a relapse does occur, you should not immediately blame the surgeon, as there are other reasons.
Practice shows that if adenotomy is performed at an earlier age, then the likelihood of relapse is higher. It is more expedient to carry out an adenotomy at children after three years. However, in the presence of absolute indications, the operation is performed at any age.
Most often, relapses occur in children who suffer from allergies. It is difficult to find an explanation for this, but experience proves that this is so.
There are children who have individual characteristics, characterized by increased growth of adenoid tissue. In this case, nothing can be done. These traits are genetically determined.
Very often, the presence of adenoid vegetations is combined with hypertrophy (enlargement) of the palatine tonsils. These organs are located in a person's throat, and everyone can see them. In children, parallel growth of adenoids and palatine tonsils is very often observed.
After the operation, physical activity, physical education, etc. should be excluded. for a two-week period, and preferably for one month.
Coarse, hard and hot food should be excluded from the child's diet. The advantage should be given to liquid food, high-calorie and containing fresh foods rich in vitamins. The term of such a diet is from 3 to 10 days, depending on the instructions of the doctor.
For at least three days, the child should not be bathed in hot water, soar. You should also limit exposure to the open sun, in hot and stuffy rooms.
For better healing of the surgical wound, nasal drops are prescribed to the child. It is mandatory to use vasoconstrictor drops (naphthyzinum, tizin, nazivin, glazolin, sanorin, ximelin, nazol, etc.) for at least 5 days, as well as solutions that have an astringent and "drying" effect. For this purpose, drop solutions containing silver (protargol, collargol, poviargol, etc.) are usually prescribed. The term of their application should not be less than 10 days.
An obligatory moment of postoperative care is breathing exercises, on which you will be advised by an ENT doctor.
In the evening after the operation, and sometimes in the morning, the child has a fever. As a rule, it does not exceed 38 degrees. If there is a need to reduce it, then in no case should drugs containing aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), which can provoke bleeding, be used.
After the operation, the child may experience one or two vomiting of blood clots. Sometimes there are moderate abdominal pain or stool disorders. This is due to the fact that the child during the operation can "swallow" blood, which, interacting with the environment of the stomach and intestines, causes the above changes. They pass quickly.
In most cases, immediately after the operation, there is a noticeable improvement in nasal breathing, but in the following days, the child may develop nasality, nasal congestion, "squishing in the nose." This is due to the presence of postoperative edema in the mucous membranes, which subsides by the 10th day.